Understanding the Core Differences: Solar System vs Photovoltaic System
Fundamental Definitions
A solar system encompasses all technologies harnessing solar energy for practical applications. This includes:
- Photovoltaic conversion (sunlight to electricity)
- Solar thermal systems (heat generation)
- Passive solar architecture
- Concentrated solar power
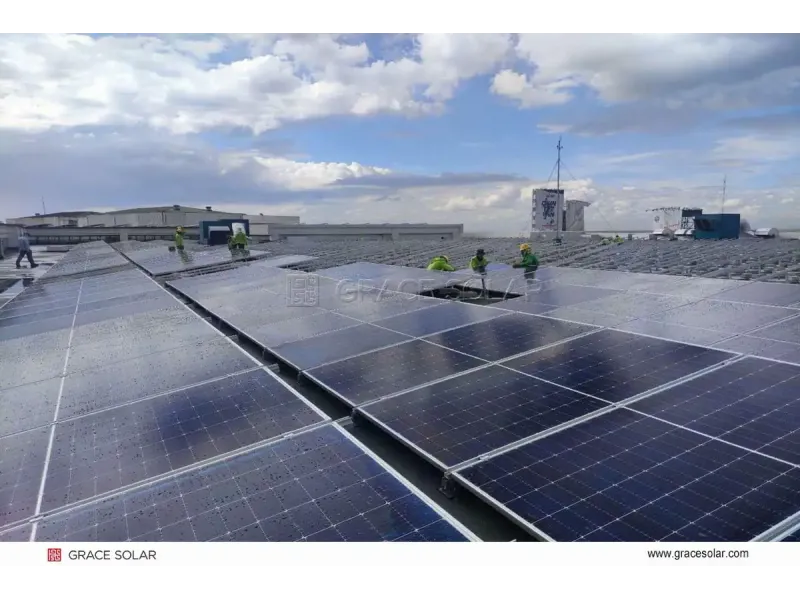
A photovoltaic system specifically converts sunlight directly into electricity using semiconductor technology. These systems feature solar panels and supporting components like inverters and tracking mounts to optimize energy capture.
Technology Comparison
Solar Thermal Systems
Function: Sunlight → Heat → Mechanical → Electricity
Efficiency: 14-22% (concentrated plants)
Applications: Large-scale power plants, water heating
Photovoltaic Systems
Function: Sunlight → Direct Electricity (PV Effect)
Efficiency: 15-22% (commercial panels)
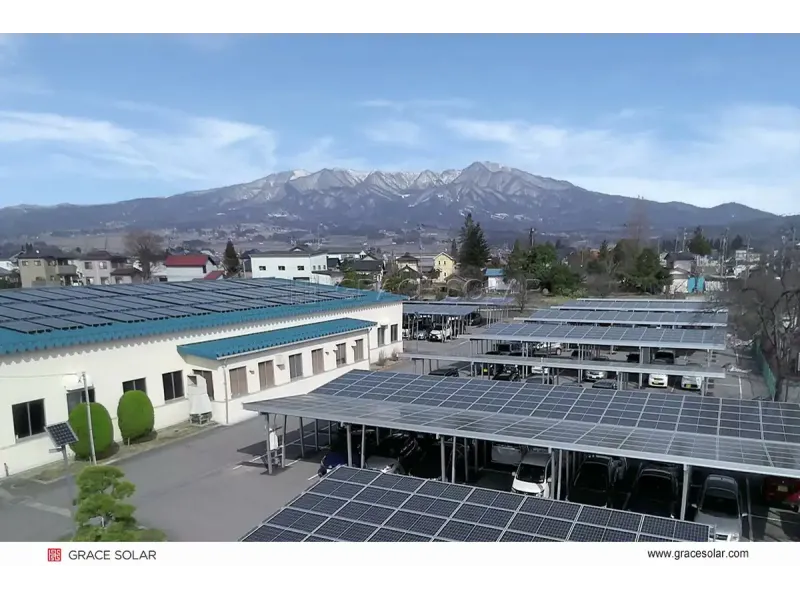
Applications: Residential, commercial, utility-scale with tracking
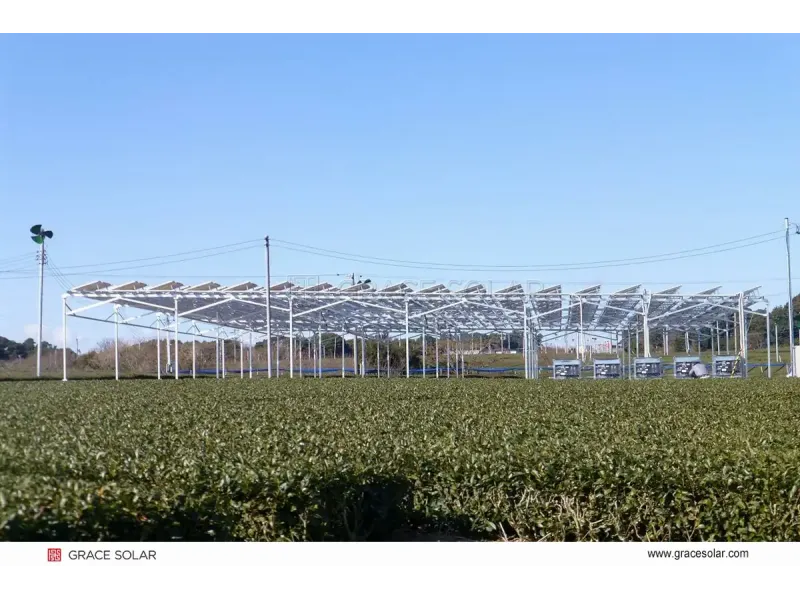
Performance Enhancement with Tracking Technology
Modern single-axis solar tracking systems can increase energy yield by 25-35% compared to fixed systems. Advanced dual-axis trackers optimize sun positioning throughout the day, with features like:
Tracking System Advantages
- AI-powered sun position algorithms
- Weather-adaptive cloud tracking strategies
- Terrain adaptability up to 20% slope
- Automatic wind protection mechanisms
- Compatibility with MPPT technology
Application Comparison
| Solar Technology | Typical Installations | Output Efficiency |
|---|---|---|
| Thermal Solar | Utility plants (50-400MW) Industrial heating | 60-70% thermal efficiency |
| Standard PV Systems | Rooftop residential Fixed ground-mount | 15-22% panel efficiency |
| Tracking PV Systems | Commercial solar farms Utility-scale plants | +30% energy generation |
Choosing the Right Solution
When considering solar implementation through EPC solutions, evaluate:
- Energy needs: Thermal requirements vs electrical demand
- Space constraints: Ground availability for trackers
- Climate factors: Solar irradiation patterns
- Tracking benefits: ROI of 2-axis systems vs fixed mounts
Advanced automatic tracking systems now incorporate predictive algorithms and wireless monitoring, representing the cutting edge in photovoltaic efficiency enhancement for commercial and utility applications.