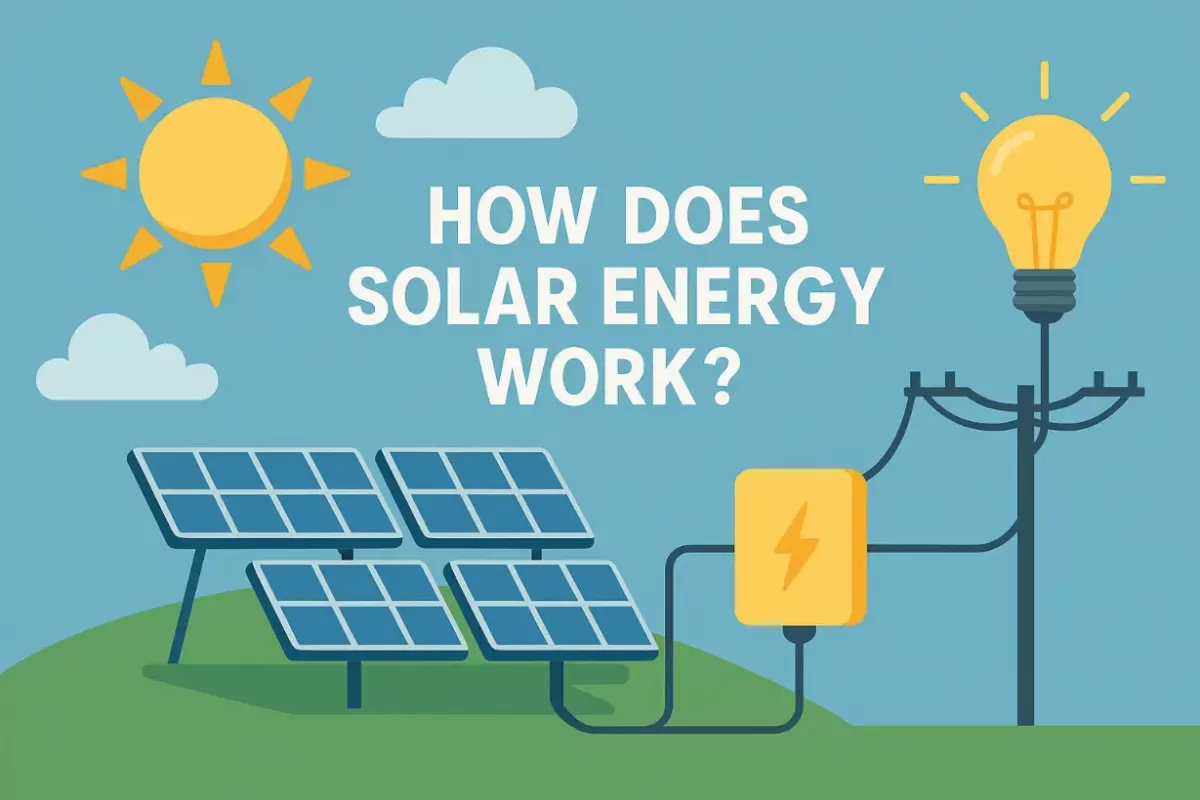
How Solar Energy Works: Step-by-Step Guide to Photovoltaic Power
The Photovoltaic Effect Explained
Solar panels work through a scientific phenomenon called photovoltaics. Each PV cell contains two layers of silicon (positive and negative) that form an electric field. When sunlight hits the cell:
- Photons strike silicon atoms, releasing electrons
- Electric field pushes freed electrons into directional flow
- Metal conductive plates collect electrons as direct current (DC)
Critical System Components
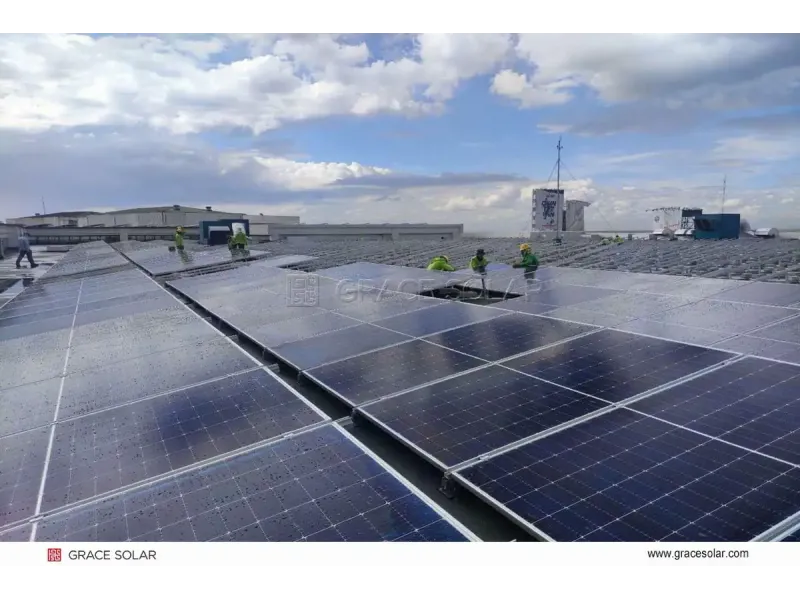
Every solar installation requires three core elements:
1. Solar Panels
Monocrystalline or polycrystalline silicon modules convert 15-22% of sunlight into electricity.
2. Inverters
Transform raw DC electricity into 120V/240V AC power for household appliances.
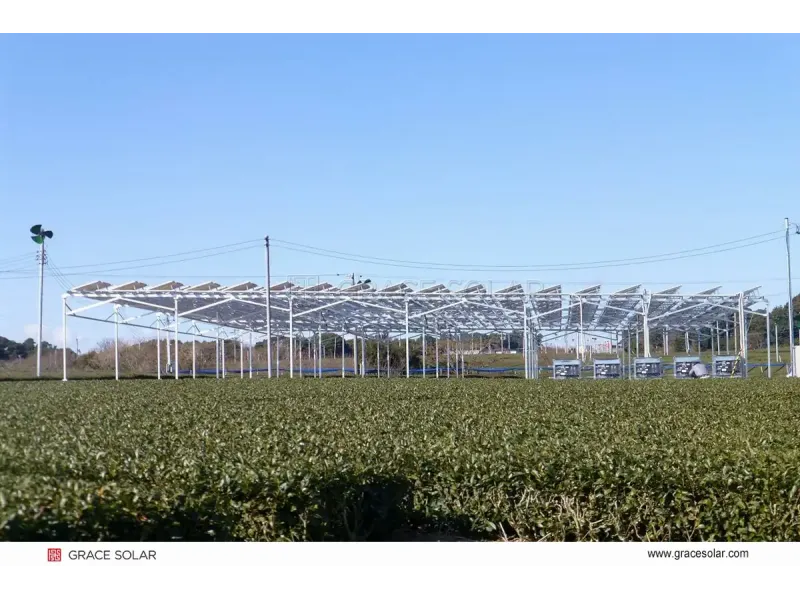
3. Mounting Infrastructure
Precision-engineered structures like single-axis trackers boost energy yield by 25-35% through optimal sun alignment. Companies like Grace Solar specialize in AI-enhanced mounting solutions validated by wind tunnel testing and international certifications.
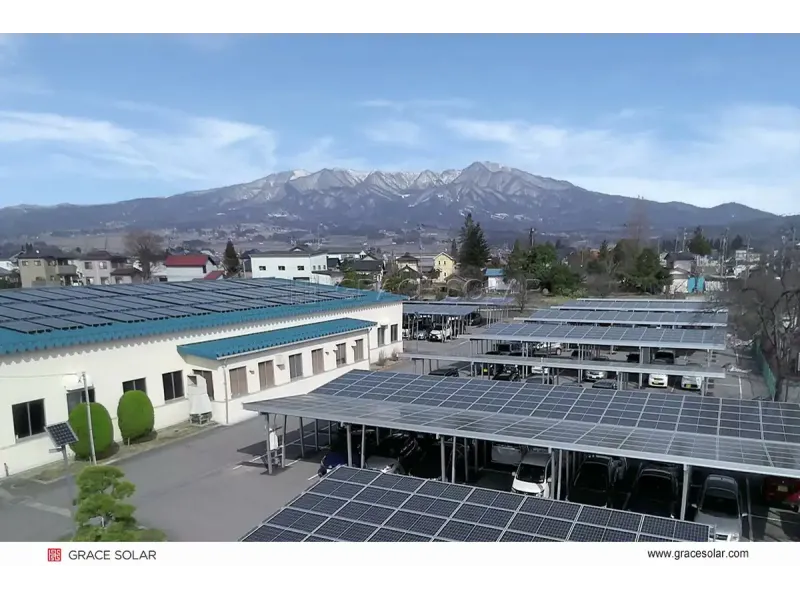
Grace Solar Case Study: 48GW Global Impact
With installations in 100+ countries, Grace Solar's mounting systems support projects from residential rooftops to utility farms. Their patented GS-Light tracker features:
- Real-time sun-position algorithms
- Wind resilience up to 140 mph
- 25-year structural warranty
Proven through global EPC partnerships, these solutions deliver 15% faster ROI.
Energy Flow Process
Maximizing Solar Efficiency
Proper installation affects system performance more than panel quality. Key considerations:
| Factor | Impact | Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Tilt Angle | ±30% energy variance | Adjustable mounting systems |
| Shading | 50%+ production loss | Micro-inverters/smart tracking |





